
Before performing an arthroscopy, the orthopedist thoroughly diagnoses the patient to establish the specific source of the problem and the best course of action. Imaging exams are usually carried out before to surgery. Before arthroscopic orthopaedic surgery, imaging tests including X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, ultrasonography, etc. are frequently used.
The orthopaedic surgeon goes over the patient's treatment choices after the diagnosis has been verified. Depending on the type of surgery being performed and the joint being operated on, arthroscopic surgery may be carried out under general anaesthesia or regional anaesthesia.
The surgeon creates a small incision (3–4 mm, about the size of a buttonhole) to insert the scope and surgical tools once the anaesthesia has taken effect. In most cases, the procedure is finished with little to
The following preparation procedures should be carried out before having arthroscopic surgery:
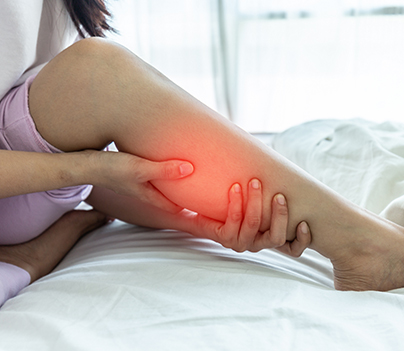
After surgery, is a homecare attendant required?
Although it is not essential following simple arthroscopic surgeries like shoulder arthroscopy, carpal tunnel release, etc., having a homecare attendant might help the patient recover faster.
Will arthroscopy make my pain go away entirely?
After arthroscopic surgery, the patient's discomfort often goes away within a few days, especially if they continue taking their meds and receiving physical therapy.
What materials make up an arthroscope?
An arthroscope is a tiny, narrow tube with a fiber-optic camera and torch attached to one end since arthroscopy refers to looking into a joint.
What percentage of arthroscopic surgeries are successful?
The success rate of arthroscopic surgery is almost 90% since there are little hazards involved and because the majority of patients just need to make minor lifestyle adjustments afterward. surgical procedures Elbow surgery ankle and foot arthroscopy wrist and hand arthroscopy Hip arthroplasty Knuckle arthroscopy Surgery on the shoulder
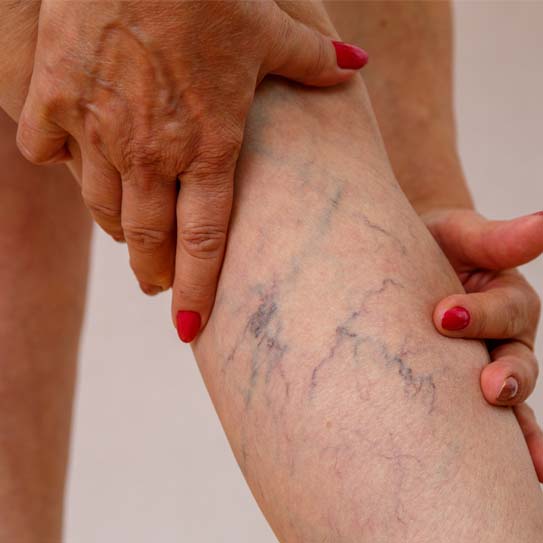
Also known as endovenous laser treatment or EVLA, this is a minimally invasive ultrasound-guided procedure that involves the use of ultrasound images and laser fiber in order to kill the delicate lining of the veins. After a few days following the procedure, the body absorbs the dead tissues, closing off the abnormal veins with minimal or no discomfort. This is one of the most commonly preferred methods as it involves far fewer complications, and the recovery time, as well as the success rate of this method, is much faster and higher than that of any surgical process.
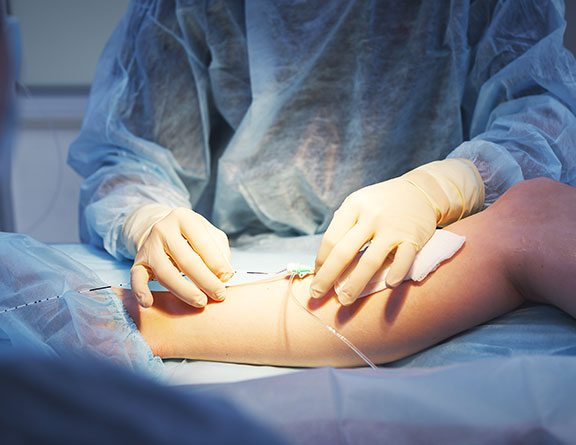
Also known as endovenous laser treatment or EVLA, this is a minimally invasive ultrasound-guided procedure that involves the use of ultrasound images and laser fiber in order to kill the delicate lining of the veins. After a few days following the procedure, the body absorbs the dead tissues, closing off the abnormal veins with minimal or no discomfort. This is one of the most commonly preferred methods as it involves far fewer complications, and the recovery time, as well as the success rate of this method, is much faster and higher than that of any surgical process.
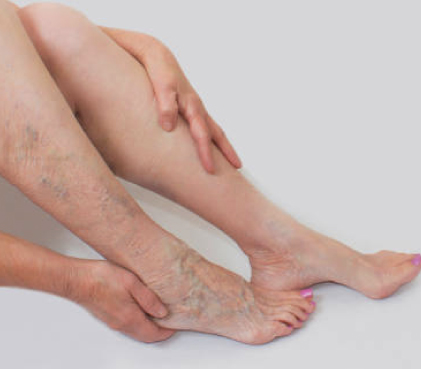
Also known as endovenous laser treatment or EVLA, this is a minimally invasive ultrasound-guided procedure that involves the use of ultrasound images and laser fiber in order to kill the delicate lining of the veins. After a few days following the procedure, the body absorbs the dead tissues, closing off the abnormal veins with minimal or no discomfort. This is one of the most commonly preferred methods as it involves far fewer complications, and the recovery time, as well as the success rate of this method, is much faster and higher than that of any surgical process.