
Either a cholesteatoma or a serious mastoid infection can be treated with a mastoidectomy. Since its symptoms are sometimes mistaken for those of other ear infections and issues, your ENT specialist must make a thorough diagnosis before developing a treatment strategy.
Your surgical therapy may change a bit depending on the seriousness of your disease. A straightforward mastoidectomy just removes the diseased portion of the bone, leaving the ear canal unaffected. To retain hearing function, your surgeon might need to connect your ear canal and mastoid bone if you require major surgery. This would include expanding the ear canal. A radical or modified mastoidectomy is the medical term for this procedure.
You should follow the given instructions to prepare for your mastoid ear surgery:
After a mastoidectomy, are I still susceptible to ear infections?
A relatively small percentage of mastoidectomy surgeries fail, with a success rate of between 80 and 90 percent. You may sometimes get small ear infections, but you may readily treat them with medicine.
How long after the mastoid operation will my ear require dressing?
After two days, you can take off your dressing, but you need to watch out that water and other foreign objects don't go inside your ear canal. To keep the ear canal closed while showering, use cotton that has been infused with antibiotics or Vaseline.
Do I require tympanoplasty along with my mastoidectomy procedure?
You could require a tympanoplasty with mastoidectomy if you also have a perforated eardrum and a mastoid/middle ear infection. You will recuperate within 6 to 8 weeks following the simultaneous procedure.
Which medical professional should I see for a mastoidectomy?
Consult an ENT specialist (ear, nose, and throat doctor) if you have ear issues and think you might require a mastoidectomy.
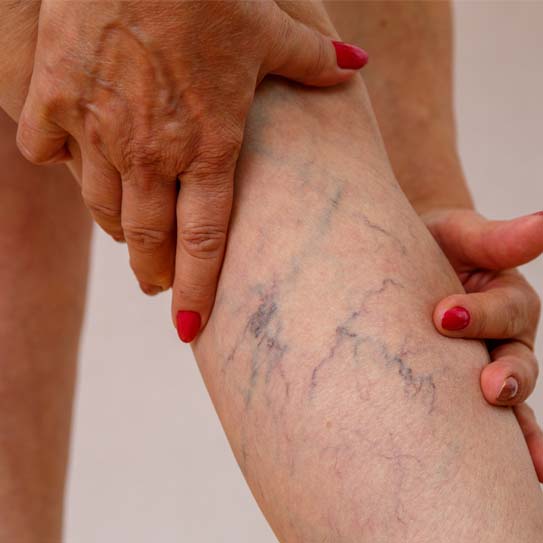
Also known as endovenous laser treatment or EVLA, this is a minimally invasive ultrasound-guided procedure that involves the use of ultrasound images and laser fiber in order to kill the delicate lining of the veins. After a few days following the procedure, the body absorbs the dead tissues, closing off the abnormal veins with minimal or no discomfort. This is one of the most commonly preferred methods as it involves far fewer complications, and the recovery time, as well as the success rate of this method, is much faster and higher than that of any surgical process.
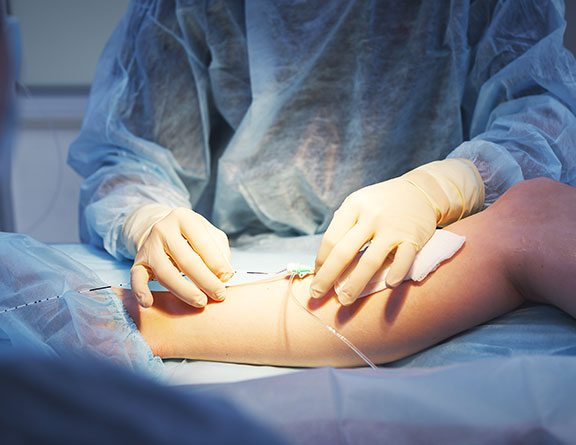
Also known as endovenous laser treatment or EVLA, this is a minimally invasive ultrasound-guided procedure that involves the use of ultrasound images and laser fiber in order to kill the delicate lining of the veins. After a few days following the procedure, the body absorbs the dead tissues, closing off the abnormal veins with minimal or no discomfort. This is one of the most commonly preferred methods as it involves far fewer complications, and the recovery time, as well as the success rate of this method, is much faster and higher than that of any surgical process.
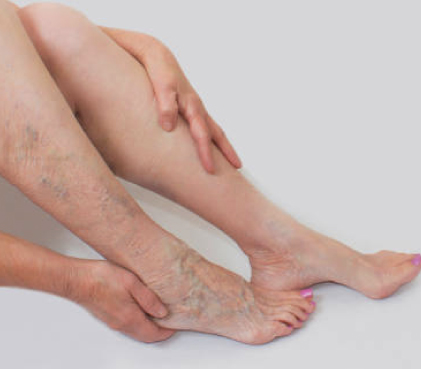
Also known as endovenous laser treatment or EVLA, this is a minimally invasive ultrasound-guided procedure that involves the use of ultrasound images and laser fiber in order to kill the delicate lining of the veins. After a few days following the procedure, the body absorbs the dead tissues, closing off the abnormal veins with minimal or no discomfort. This is one of the most commonly preferred methods as it involves far fewer complications, and the recovery time, as well as the success rate of this method, is much faster and higher than that of any surgical process.